
This study paves the way to a new investigation modality of micrometric systems, combining high lateral resolution with excellent spectral quality, essential in the field of Cultural Heritage as well as in the wider area of materials and forensic sciences. A microscopes resolution limit, d, can be found by the following formula: d 0.61 / NA, where is the wavelength of light coming from the object.
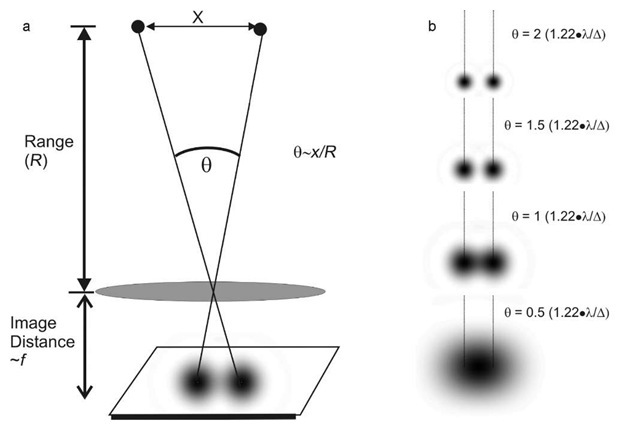
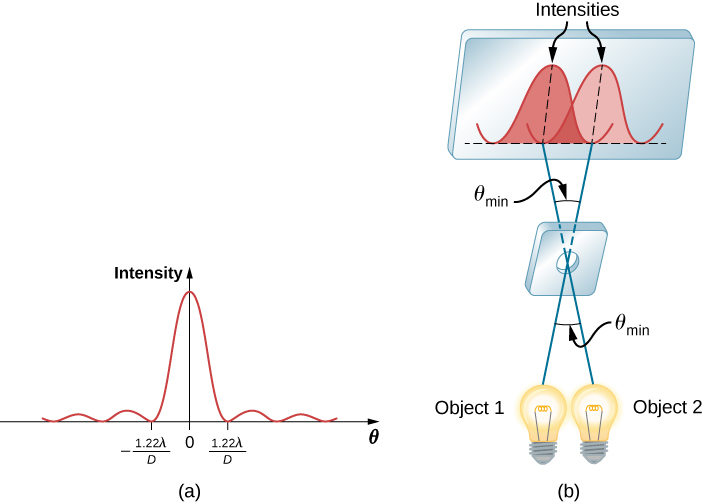
m 0 m 1 m 2 m -1 The dots on a CD are equally spaced (although some are missing, of course), so it acts like a diffraction grating. The method has been first validated on mock-ups and then successfully applied on cross-sectional samples from real artworks: Leonardo da Vinci's mural painting, characterised by a few micrometers thin sequence of organic and inorganic layers, and an outdoor marble statue, with a complex sequence of decay products on its surface. Real diffraction gratings Diffracted white light White light diffracted by a real grating. This study demonstrates the high micro-ATR-FTIR setup performances in terms of lateral resolution, spectral quality and chemical image contrast using a new laboratory instrument equipped with a single element detector. The size of the central ridge is determined by the condition that the differences in optical paths should be comparable with the wavelength. The light from the two stars will create a double slit diffraction pattern on the screen. Suppose we have an infinite screen at x0. Figure 1 - Resolution Limit Imposed by Wave Nature of Light Formula 1 - Radius of the Diffraction Airy Disk in the Lateral (x,y) Image Plane. According to Rayleigh’s Criterion For two nearly equal wavelengths 1 and 2 between which a diffraction grating can just barely distinguish, the resolving power R of the grating is defined as: R / Thus,a grating that has a high resolving power can distinguish small differences in wavelength. This method can be an effective analytical alternative when the layer thickness requires high lateral resolution, and fluorescence or thermal effects prevent the deployment of conventional analytical techniques such as micro-Raman spectroscopy. Let us consider two stars located at (-L,h/2) and (-L,-h/2). This paper is aimed at demonstrating the potentiality of high resolution Attenuated Total Reflection Fourier Transform Infrared micro-mapping (micro-ATR-FTIR) to reconstruct the images of micrometric multi-layered systems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
